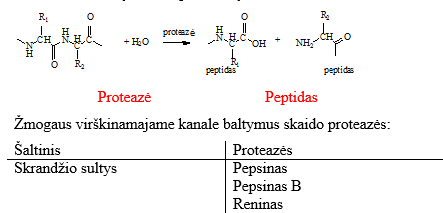
Proteases
There are hydrolases (EC 3.4.2) that break down peptide bonds of proteins and other compounds by attaching a water molecule, performing proteolysis.

Proteases found in lysosomes are called cathepsins.
An enzyme group that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a protein molecule into smaller parts. Usually complexes of complex peptidases and proteinases that break down a protein substrate. Depending on the products formed from a protein molecule after the action of proteases, they are divided into endopeptidases and exopeptidases. Endopeptidases hydrolyze the peptide bonds of a protein molecule inside it, resulting in many polypeptides. An example of these can be digestive tract enzymes – pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, gastricsin, etc. These enzymes are collectively called proteinases. Enzymes that hydrolyze the hydrolysis of terminal amino acids are called exopeptidases. Exopeptidases that separate a free amino acid from the peptide N-terminus are called aminopeptidases, and those that separate the amino acid from the peptide C-terminus are called carboxypeptidases. Dipeptides are cleaved by specific dipeptidases.
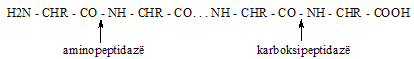
Source | Glossary of Most Commonly Used Biomedical Terms and Concepts | Lithuanian University of Health Sciences | Academician Professor Antanas Praškevičius, Professor Laima Ivanovienė
