Nicotine
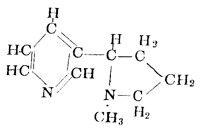 This is an alkaloid composed of pyridine and N-methylpyrrolidine rings. It is a colorless, transparent, oily liquid with a sharp odor and burning taste. It is extracted from tobacco, where it constitutes about 1.1–3.0% of dry mass. Nicotine is synthesized in roots and accumulated in leaves. It serves a protective function against insects in plants, hence it was previously used as an insecticide. It is a substance that strongly affects the central nervous system, inducing a certain short-term alert state. Highly toxic: from a few drops (about 0.05 g, the amount of nicotine in 200 g of tobacco) a person can die due to paralysis of the brain’s respiratory center. Small doses stimulate the nervous system, larger doses suppress it, disrupt breathing, heart rate, and increase blood pressure. Nicotine yields nicotinic acid, which is used as an insecticide and fungicide.
This is an alkaloid composed of pyridine and N-methylpyrrolidine rings. It is a colorless, transparent, oily liquid with a sharp odor and burning taste. It is extracted from tobacco, where it constitutes about 1.1–3.0% of dry mass. Nicotine is synthesized in roots and accumulated in leaves. It serves a protective function against insects in plants, hence it was previously used as an insecticide. It is a substance that strongly affects the central nervous system, inducing a certain short-term alert state. Highly toxic: from a few drops (about 0.05 g, the amount of nicotine in 200 g of tobacco) a person can die due to paralysis of the brain’s respiratory center. Small doses stimulate the nervous system, larger doses suppress it, disrupt breathing, heart rate, and increase blood pressure. Nicotine yields nicotinic acid, which is used as an insecticide and fungicide.
Smoking is the burning of substances (usually dried tobacco plant leaves) and inhaling the resulting smoke. Smoking typically refers to tobacco smoking. Narcotic or psychotropic substances efficiently transfer from smoke into the bloodstream through the lungs. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which has a short-term stimulating effect but creates a strong physiological and psychological dependency. It has been found that on average, smoking 15 cigarettes causes one point mutation in the human genome. Malignant tumor cells have about 10–30 thousand point mutations. Smoking is one of the main risk factors for many lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, and lung tumors). People who smoke suffer from chronic bronchitis 5.5 times more and from lung tumors 10 times more than non-smokers. Smokers have a higher mortality rate from lung diseases than non-smokers. Passive smoking is when a non-smoker inhales the smoke exhaled by a smoker. Exhaled smoke contains carcinogens and other harmful substances, posing a health risk. Secondhand smoke in public places is considered a public health issue.
Source | Glossary of Most Commonly Used Biomedical Terms and Concepts | Lithuanian University of Health Sciences | Academician Professor Antanas Praškevičius, Professor Laima Ivanovienė
