Ibuprofen
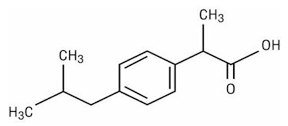 According to IUPAC, (RS)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, used to reduce fever or pain. Its effect is similar to aspirin, but acts faster and for a shorter period. It is believed to work by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX1 and COX2) and thus stopping the natural synthesis of prostaglandins in the body. Only the S enantiomer is active. It is usually taken in fairly large quantities. 1.2 g is the maximum safe daily dose.
According to IUPAC, (RS)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, used to reduce fever or pain. Its effect is similar to aspirin, but acts faster and for a shorter period. It is believed to work by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX1 and COX2) and thus stopping the natural synthesis of prostaglandins in the body. Only the S enantiomer is active. It is usually taken in fairly large quantities. 1.2 g is the maximum safe daily dose.
Source | Glossary of Most Commonly Used Biomedical Terms and Concepts | Lithuanian University of Health Sciences | Academician Professor Antanas Praškevičius, Professor Laima Ivanovienė
