Gout
Gout – a chronic metabolic disorder when there is a disturbance in the metabolism of uric acid.
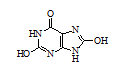
Uric acid (2,6,8-trihydroxypurine)
Urates accumulate in and around the joints, causing chronic gouty arthritis. The concentration of urates depends on the pH of the environment. The lower the pH, the worse the solubility of uric acid (urates). Under physiological conditions, at a temperature of 37��C, the concentration of sodium urate in the blood is 2-6 mg/dl. With an increased concentration (more than 7 mg/dl), sodium urate crystals accumulate in soft tissues, especially in and around the joints. This leads to the formation of so-called tophi, causing inflammatory reactions and acute gouty arthritis. In the case of hyperuricemia, urate stones can form in the kidneys. The disease is characterized by acute and chronic joint inflammations, causing joint pain and dysfunction. There are no symptoms typical of arthritis in the initial stages of the disease. Factors influencing the transition from asymptomatic hyperuricemia to primary gout include:
– patient’s age and duration of hyperuricemia; gout is not typical in young people;
– genetic predisposition, alcohol consumption can trigger arthritis attacks, obesity, certain medications (thiazides), lead poisoning.
Synovial joint fluid is a poorer solvent for urate crystals than plasma, so urates accumulate in the joint fluid. With prolonged hyperuricemia, crystals accumulate in the joint cartilage. Chemotaxis leads to the accumulation of neutrophils and macrophages in the joints and synovial membranes. Phagocytosis of crystals promotes the synthesis of harmful free radicals and leukotrienes. Neutrophils activate hydrolytic enzymes, and macrophages secrete various mediators that cause an inflammatory reaction and joint damage. Joint dysfunctions also occur. Hypersecretion of urates can be secondary, for example, in cancer or psoriasis. Gout is treated with xanthine oxidase inhibitors, such as allopurinol. By inhibiting this enzyme, uric acid is not formed from xanthine, and the final product of purine catabolism is xanthine, which is more soluble in water than uric acid, preventing crystal formation. Gout is more common in men. Many animal-derived products, especially in fish roe, contain purines – substances that are converted into uric acid in the body.
.png)
Allopurinol Xanthine
Source | Glossary of Most Commonly Used Biomedical Terms and Concepts | Lithuanian University of Health Sciences | Academician Professor Antanas Praškevičius, Professor Laima Ivanovienė
