Disacharids
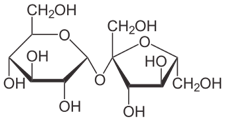
Disaccharides are two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond. They are composed of two identical or different monosaccharide molecules. There are not many naturally occurring independent saccharides. The most common disaccharides are: maltose, cellobiose, lactose, sucrose, trehalose. In nature, there are many more disaccharide fragments found in many plant and bacterial glycosides. Disaccharides are hemiacetals, i.e., O-glycosides, where the residue of the second molecule is an aglycone. Hemiacetals hydrolyze easily, so monosaccharides are formed from disaccharides: maltose breaks down into two glucose molecules; sucrose breaks down into glucose and fructose.
Source | Glossary of Most Commonly Used Biomedical Terms and Concepts | Lithuanian University of Health Sciences | Academician Professor Antanas Praškevičius, Professor Laima Ivanovienė
